Solder pasteReflow soldering is a motherboard-level interconnection method used in the surface mount assembly process. This welding method perfectly combines the available spot welding features, including easy processing, wide compatibility with these surface mount designs, and high spot welding reliability to reduce costs. However, when reflow soldering is used as the most important means of interconnecting at the surface mount component level and the board level, further improving solderability itself is a challenge. In fact, whether reflow soldering technology can withstand this challenge will affect whether solder paste can continue to be the main surface mount stainless steel material, especially with the continuous innovation of ultra-fine pitch technology. Next, we will discussSeveral core issues that stimulate the improvement of reflow soldering performance are explained to you by the solder paste manufacturer below:
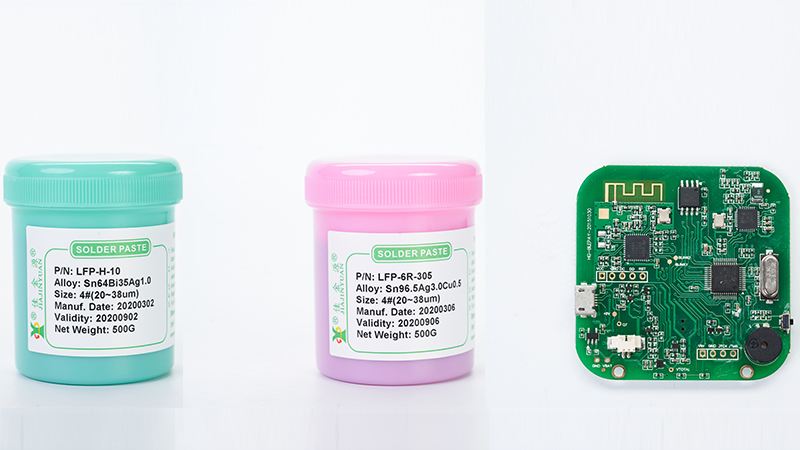

Fixation of the bottom surface components
Double-layer reflow soldering has been in use for several years. Here, first, the first side is printed and wired, components are installed and reflow, and then the other side of the circuit board is flipped over for cleaning. So it is more economical. Some processes ignore the reflux of the first surface, but reflux the top surface and the bottom surface simultaneously. A typical example is that only small components, such as chip capacitors and chip resistors, are fixed on the bottom surface of the circuit board. BecausepcbThe design of circuit boards is becoming increasingly cumbersome, and the components fixed on the ground are getting larger and larger. Therefore, component separation on the reflux ground becomes an important issue. It seems that the phenomenon of component dropping is due to the insufficient vertical fixing force exerted by the molten solder on the component during reflow, and the insufficient vertical fixing force can be attributed to the increase in component weight, poor solderability of the component, insufficient wettability of the solder, or insufficient amount of solder, etc. Steam, the first factor is the most essential process factor. If the components fall off after the improvement of the last three various factors, surface mount adhesives must be used. It seems that the use of adhesives will reduce the self-bonding effect of components during reflow.
The spot welding has not been complete yet.
Viscosity has a thorough spot solder to form a spot solder bridge between adjacent leads. Generally speaking, the factor that can cause solder paste to collapse due to steam energy can also lead to incomplete spot solder. These factors include:1.The speed of high temperature is too fast.;2.The thixotropy of the solder paste is too poor or the recovery of the solder paste vapor is too slow after shearing.3The metal load or solid content is too low;4The powder particle size distribution is too wide;5.It seems that if the surface pressure of the flux is too small, the collapse does not necessarily lead to insufficient spot welding. During the reflow soldering process, the insufficiently melted solder may crack under the push of surface pressure, and the loss of solder will make the incomplete spot welding even more severe. In this case, the large amount of solder accumulated in a certain area due to solder loss will cause the molten solder to be too much and not easy to fall off.
In addition to the factors that cause solder paste slump, the following various factors are also common causes of incomplete spot soldering:
1Compared with the space between the solder joints, too much solder paste has accumulated;
2The heating temperature is too high;
3The heating speed of solder paste is faster than that of circuit boards.
4The wetting speed of the flux is too fast;
5The flux vapor pressure is too low;
6The solvent content of the flux is too high;
7The softening point of the flux resin is too low.
For reflux processes that do not require cleaning, to achieve decorative or functional effects, a low margin is usually required. Examples of functional requirements include "detecting and testing the wear-resistant surfacing layer through flux residue tested in the circuit, and making electrical contact between the insert and the wear-resistant surfacing layer or between the insert and the through hole near the reflow soldering point". Generally speaking, a large amount of flux residue leads to excessive residue covering the metal surface to be electrically contacted, which will hinder the formation of the electrical connection. Due to the increase in circuit density, such problems have received increasing attention from people.
It seems that low-residue solder paste that does not require cleaning is the ideal solution to meet this requirement. It seems that the key elements related to this softening melt make the problem even more difficult. To predict the solderability of low residual solder paste under different inert reflow environments, a semi-empirical model is proposed. This model predicts that solderability will continuously increase due to the decrease in oxygen content and then gradually stabilize relatively. The specific results of the experiment show that due to the decrease in oxygen concentration, the surface quality and wetting ability of the solder paste will increase. In addition, the surface quality will also increase due to the increase in the solid content in the solder paste. The model proposed in the experimental report has the principle of comparability, which strongly proves the efficiency of the model and is applicable to predicting the solderability of solder paste and materials. Therefore, it can be concluded that an inert reflux environment is generally adopted to enable the rapid use of low residual solder without cleaning.





 Tel:+86 0755 88366766
Tel:+86 0755 88366766 Phone:+86 18938660310
Phone:+86 18938660310 Email:sales@jjyhanxi.com
Email:sales@jjyhanxi.com Address:13/F,12/F, Building No. B,Qinghu Technology Park,Qingxiang Rd.,Qinghu Community, Longhua Subdistrict,Longhua District,Shenzhen City,GUANGDONG Province,P.R.C.(518027)
Address:13/F,12/F, Building No. B,Qinghu Technology Park,Qingxiang Rd.,Qinghu Community, Longhua Subdistrict,Longhua District,Shenzhen City,GUANGDONG Province,P.R.C.(518027) Guangdong Public Security Backup 44030902002666 name
Guangdong Public Security Backup 44030902002666 name
 WeChat
WeChat WeChat official account
WeChat official account
